Nessus is a security scanner of vulnerability. Lately there was a lot of discussion about this topic. First of all little bit of history. Project Nessus was originaly under GPL licence, but somebody smart has closed the source codes and GPL was over. The project continued as Tenable Nessus and free version (GPL licence) under name GNessUs. But this one died out after a year abd the application goes on as OpenVas. Parallel GPL project is based on the last opened source code Nessus, therefore the OpenVas is today compatible with Nessus. There is OpenVas client connected to Nessusd on the picture.
Nessus is a security scanner of vulnerability. Lately there was a lot of discussion about this topic. First of all little bit of history. Project Nessus was originaly under GPL licence, but somebody smart has closed the source codes and GPL was over. The project continued as Tenable Nessus and free version (GPL licence) under name GNessUs. But this one died out after a year abd the application goes on as OpenVas. Parallel GPL project is based on the last opened source code Nessus, therefore the OpenVas is today compatible with Nessus. There is OpenVas client connected to Nessusd on the picture.
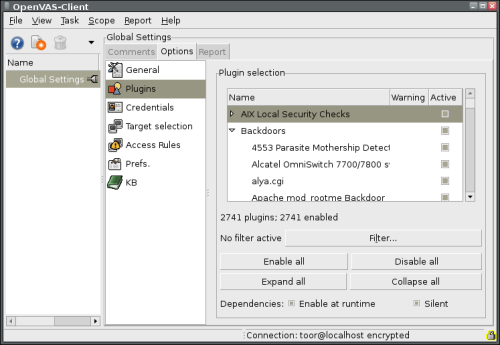
Nessus
Few remarks. First and foremost Nessus is a (same as OpenVas) “client – server” application. With GUI client part, without installed nessusd daemona (locally or far) you can´t do anythig. The next problem is that the application developer closed the source codes and even though Nessus can detect things such as CGI vulnerability, backdoors, analyze far access to files, redundant network services, Denial of Service attacks (DoS), test service finger, root shell or do the penetration test of firewall, FTP, SMTP services, or scann ports one of five scanners, lots of other important things are for money.
Nessus works on plug-in base (originaly written in NASL Nessus Attack Scripting Language). At this moment there is 1300 of them but they are for money. The price is 1200 $. For free you can use a set of extension for one week. What I don ´t understand is a list of around 2700 plugins, available in istallation in Linux distribution Ubuntu (!?).
Nessus Installation
On home page of application Nessus you can download all packages and after registration you can get the mentioned test extention. In Ubuntu repozitory there is available a client application and also a server part Nessusd. Everything can be installed by Synaptic (no need to describe further).
Nessus Configuration
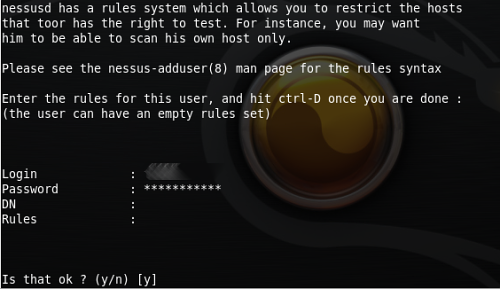
After the installation it is neccessary by the command nessus-adduser add the user and choose a way how to autentificate towards the system (password or certificate). Other commands are nessus-check-signature, nessus-adduser, nessus-rmuser, nessus-mkcert. Then just run the interface, log in as registered user into the system and a lot of offers appear that can be configurated.
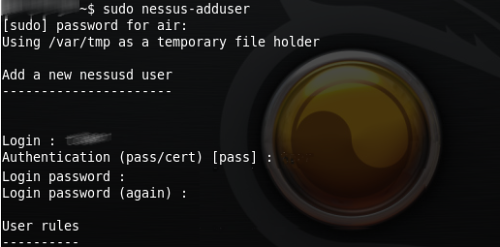
Configuration dialog allows inserting other parameters
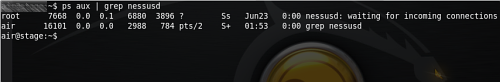
Command [code]ps aux | grep nessusd[/code] writes out activity of services connected to daemon Nessusd
Then comes the computer scann.
Extensions – Plugins
The list of extention is logicaly divided, it inludes categories, each category includes a list of plugins. Them after marking an availabe choice.
Categories
AIX Local Security – Backdoors (trojan horse) – CGI vulnerability – CGI vulnerability XSS – CISCO – Database – Debian Locall Security Audit – Default Unix Acounts – Denial from Service – FTP server – Service Finger vulnerability – Firewals – GPL Feed – Far shell acquisition – Far root acquisition – Gentoo Locall Security Audit – MacOS Locall Security Audit – Netware – Peer-To-Peer file sharing – RPC – Red Hat Locall Security Audit – Remote File Aceess (far access to files) – SMTP problems – SNMP – Useless Servers (redundant services) – Webo servers – Windows
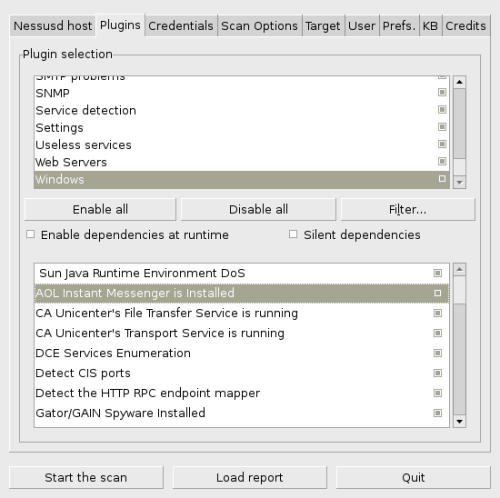
At every extention you can separately configure timeout and display dependencies. In plug-in interface there is perceivable the revision and information about vulnerability for which the plugin was written.
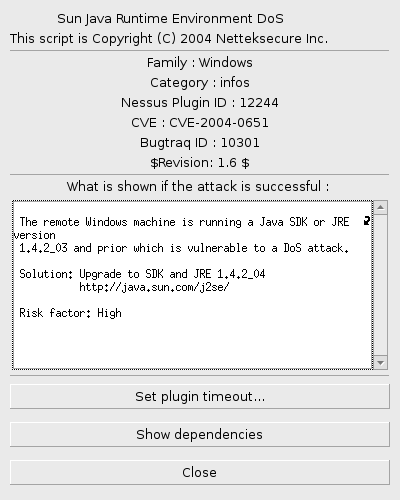
List of Nessus plugins
The list includes more then 2700 records so it was placed in Wiki under name Nessus Plug-In.
Similar Posts:
- Exploiting with Metasploit – Hacking Windows XP Box
- WLAN Hacking with WEPKR plug-in
- BackTrack 5 R2 release
- Abhinav Singh Metasploit Penetration Testing Cookbook
- BackTrack 5 R3 release blackhat edition
- Bluetooth Security & Vulnerabilities
- Installing ipkg & mc (Midnight Commander & more) NAS Synology DS212j
- WEP Crack – video tutorial for beginners
- Wired keyboard eavesdropping video
- BackTrack 5 Revolution released